March 3, 2026
Change Management - Overview
Enterprise Digital Change Management is committed to minimizing the impact of Change-related incidents on service quality, and improving the day-to-day operations of the Mass General Brigham organization. The Change Management process implemented at Mass General Brigham is geared to ensuring that we have adequate review, communication, and analysis of all Changes affecting the organization, as well as a process for reviewing the overall Change Management strategy. Major components of our Change Management process include our review board and our classification of Changes into Change types and subtypes.
This article includes the following sections:
High-Level Summary of the ITIL Change Management Process
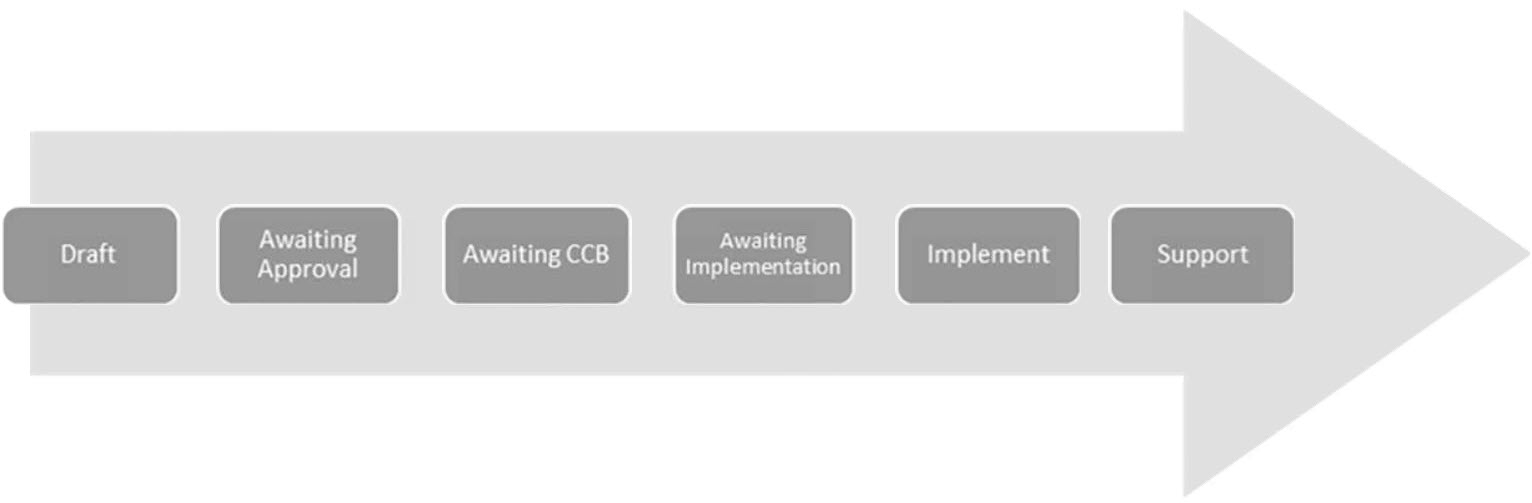
- Draft - Initiation of the process to document the Change, complete with communication, implementation, and backout plans.
- Awaiting Approval - The Change works its way through all necessary approvals.
- Awaiting CCB - A Change must be in this state before the CCB.
- Awaiting Implementation - Await the Start Date of the Change.
- Implement - Execute the Change.
- Support - Completion of all follow-up activities, including the Post-Implementation Review (PIR)
Key Terms
| Backout Plan |
A contingency plan of step-by-step instructions to minimize any disruption of service if a Change implementation does not go as planned. |
| Change |
The addition, modification, or removal of a supported service or a modification to an application or hardware. |
| Change Advisory Board (CAB) |
A strategic group that meets to provide a forum for policy and process update discussions. It is responsible for giving expert advice regarding Change Management governance. It consists of the permanent members of the CCB. |
| Change Control Board (CCB) |
An operational group that meets each Wednesday to give expert advice to Change Management on the implementation of Changes. It includes representatives from all areas within Mass General Brigham, including site leadership, configuration owners, application owners, technical leadership, as well as any individual with stakeholder interest. |
| Change Freeze |
A block on Production Changes impacting entities or facilities, applications, and resources during the major event window. |
| Change Management |
The standardized methods and procedures used for the efficient and prompt of all changes to control our IT infrastructure to minimize the number and impact of any related incidents upon service. |
| Change Subtype |
A categorization of a Change based on its risk and impact. |
| Change Type |
A system-calculated categorization of a Change based on its lead-time and Change subtype. |
| CMDB Management |
The main objective of the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is impact analysis. It allows us to minimize outages by connecting the people and technology items associated with services required by Mass General Brigham. |
| Compliance |
A compliant Change is a well-prepared and executed Change. It clarifies what, why, and how the Change is being executed and is reviewed by the requester after implementation. |
| Configuration Item |
Any component that needs to be managed in order to deliver an IT service. CIs are controlled through the Change process and stored in the Configuration Management Data Base (CMDB). |
| Emergency Change Control Board (eCCB) |
A subset of the Change Control Board for reviewing Expedited and Emergency Changes, as needed. . |
| Level of risk |
The caution used to implement a change successfully. When assessing risk is calculated based on the following factors: * Number of teams to implement * Prior change success * Incident history * Time to back out * Implementation window Note: At the current time, business risk is not calculated within the Change form nor documented unless by the requester within description and/or impact of the Change. However, please consider the risk to the business, of not implementing the change. Some common types of business risks include strategic, financial, clinical operations, compliance, and any other contributing factors that could have a negative impact on the business. |
| Maintenance Schedule |
A designated time period when maintenance-related Changes are scheduled to be made to a specified Configuration Item (CI). |
| Post Implementation Review (PIR) |
Review of a completed Change. The PIR should note any issues or steps taken. A PIR is required to be completed within 5 days after implementation of any Major, Significant, or Emergency Change. |
| Request for Change (RFC) |
RFCs can be entered by business users who do not have all of the required information or who may not even know what his or her specific needs might be. It can also be used between Digital groups or even within a single group, if required by team policy. |
Change Subtypes
Use this field to assess the lead-time and review requirements for a Change based on a combination of the impact and risk. Change Subtypes are as follows, based on the Risk Impact Matrix:
- Minor
- Significant
- Major
|
Risk |
Impact |
|||
|
|
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
|
Low |
Minor |
Minor |
Minor |
|
|
Medium |
Minor |
Significant |
Significant |
|
|
High |
Minor |
Major |
Major |
|
Change Types
The combination of the Change Type and the available lead-time allows us to classify changes into the following Change Types:
- Normal – Changes that allow for adequate lead-time based on the Change Type.
- Expedited – Changes that do not allow for adequate lead-time.
- Emergency – Changes with less than 30 minutes lead-time or in the past. Typically to resolve a service interruption (Incident).
- Pre-Approved - The Pre-Approved Change type provides a template for introducing low-risk, routine Changes to the Mass General Brigham environment.
